About ACEThe proceedings series Applied and Computational Engineering (ACE) is an international peer-reviewed open access series that publishes conference proceedings from various methodological and disciplinary perspectives concerning engineering and technology. ACE is published irregularly. The series contributes to the development of computing sectors by providing an open platform for sharing and discussion. The series publishes articles that are research-oriented and welcomes theoretical and applicational studies. Proceedings that are suitable for publication in the ACE cover domains on various perspectives of computing and engineering. |
| Aims & scope of ACE are: ·Computing ·Machine Learning ·Electrical Engineering & Signal Processing ·Applied Physics & Mechanical Engineering ·Chemical & Environmental Engineering ·Materials Science and Engineering |
Article processing charge
A one-time Article Processing Charge (APC) of 450 USD (US Dollars) applies to papers accepted after peer review. excluding taxes.
Open access policy
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. (CC BY 4.0 license).
Your rights
These licenses afford authors copyright while enabling the public to reuse and adapt the content.
Peer-review process
Our blind and multi-reviewer process ensures that all articles are rigorously evaluated based on their intellectual merit and contribution to the field.
Editors View full editorial board

United Kingdom

Malaysia

United Kingdom

United Kingdom
yilun.shang@northumbria.ac.uk
Latest articles View all articles
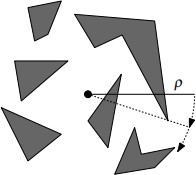
Field of view (FOV) algorithms are essential in determining the visible area of a player in 2D games. These algorithms dynamically calculate the visible areas while occluding these hidden areas, and play an important role in games such as roguelikes and stealth games. This survey summarizes three 2D FOV algorithms: ray casting, rectangle-based FOV, and recursive shadowcasting. The ray casting algorithm casts rays to determine which area was hidden from the player, which is a basic FOV algorithm. Rectangle-based FOV optimizes computation for large 2D grids by representing obstacles as rectangles, also using a quadtree to improve the access speed. Recursive shadowcasting efficiently computes the visible area by dividing the grid into 8 octants and recursively splitting the view when obstacles are encountered. This survey also mentioned how to adapt the recursive shadowcasting algorithm to 2.5D and 3D environments.

 View pdf
View pdf


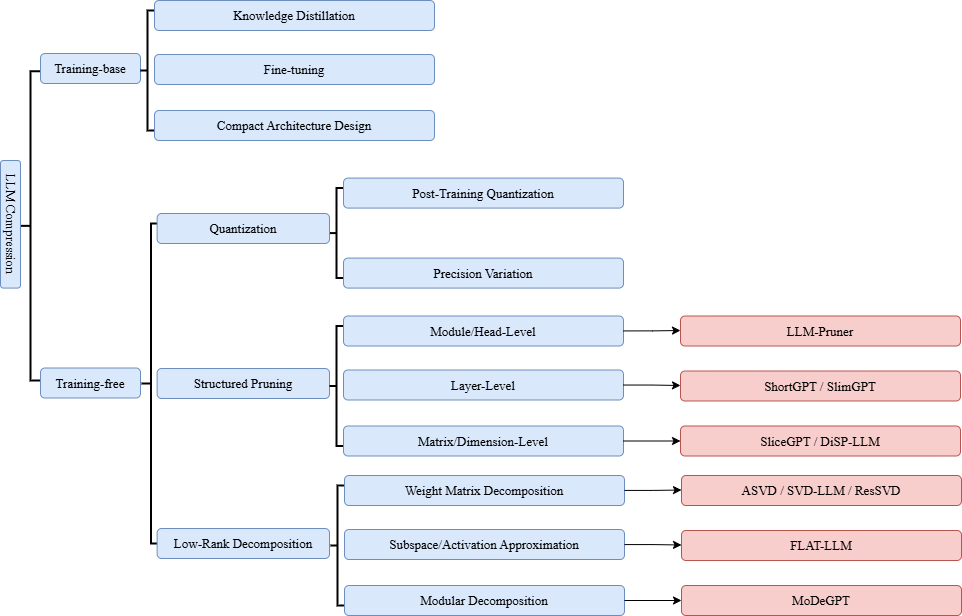
The well-known Large Language Model (LLM) compression is essential for enhancing computational efficiency, yet a systematic summary of investigation into structured pruning and low-rank decomposition remains absent in current literature. This work addresses the gap by providing a comprehensive review specifically focused on these two methodologies. Representative approaches are categorized and evaluated, including LLM-Pruner and SlimGPT for structured pruning, and ASVD and SVD-LLM for decomposition. These methods are rigorously analyzed in terms of algorithmic design, accuracy retention, and hardware adaptability. Through unified evaluation and comparative analysis, DISP-LLM and MoDeGPT are identified as the current state-of-the-art within their respective fields. Consequently, a conceptual framework is established to provide practical guidance for future research into efficient, training-free, and scalable LLM compression.

 View pdf
View pdf


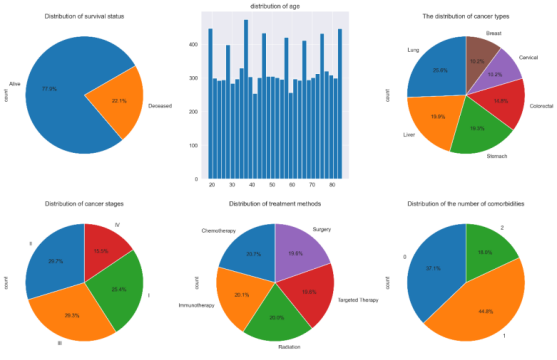
Cancer remains a major public health challenge in China. This study analyzed a multi-center cohort of 10,000 Chinese cancer patients to evaluate real-world survival outcomes and treatment effectiveness. Kaplan–Meier estimation and Cox proportional hazards regression were employed to assess associations between patient characteristics, treatment types, and overall survival. Survival analysis showed no significant difference in overall survival among six major cancer types (lung, liver, stomach, colorectal, cervical, breast) or among five treatment modalities (chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, surgery). Cancer stage was the strongest prognostic factor: patients with Stage I–II disease had 100% five-year survival, while Stage III–IV survival fell to about 6%. Metastasis, larger tumor size, and geographic region were independent risk factors for death after adjusting by other covariates, but not modality of treatment. The results highlight the importance of timely diagnosis and availability of healthcare services in different areas are important targets of China's cancer prevention programs.

 View pdf
View pdf


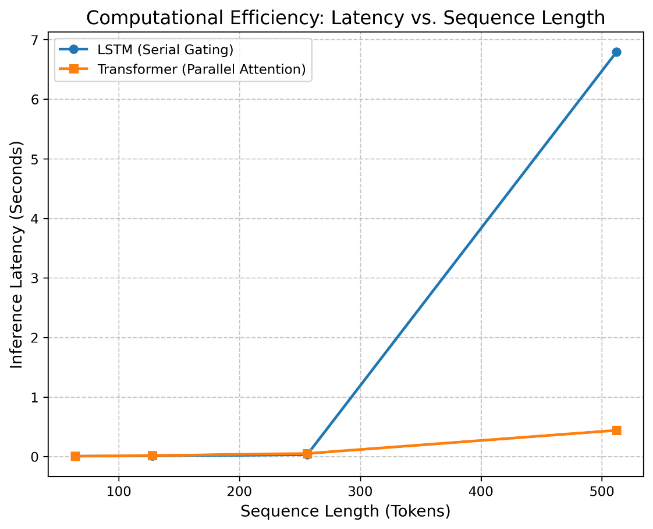
This comprehensive research synthesizes the foundational principles of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and their realization within ChatGPT, examining the ways deep learning architectures internalize profound linguistic complexity. Structural interplay is investigated. A dual-track empirical framework is systematically employed. By contrasting traditional Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks with the Transformer architecture, the first track effectively demonstrates how parallelized self-attention maintains deep semantic coherence. High-order representational accuracy is achieved. The Qwen2.5-1.5B series is analyzed. By systematically comparing "Base" and "Instruct" models to decouple intelligence origins, the second track reveals that while massive scaling creates an expansive "Cognitive Reservoir" of knowledge, Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) provides the essential "Functional Bridge" for precise, intent-driven execution. Aligned utility is realized. Ultimately, modern AI is viewed as the synergistic integration of structural efficiency, volumetric growth, and intentional refinement.

 View pdf
View pdf


Volumes View all volumes
Volume 226February 2026
Find articlesProceedings of CONF-SEML 2026 Symposium: Multimodal Data Acquisition: Applications in Physiological and Behavioral Research
Conference website: https://www.confseml.org/adana.html
Conference date: 20 May 2026
ISBN: 978-1-80590-637-7(Print)/978-1-80590-638-4(Online)
Editor: Mustafa İSTANBULLU
Volume 225February 2026
Find articlesProceedings of CONF-SPML 2026 Symposium: The Artificial Intelligence Tools & Applications
Conference website: https://www.confspml.org/chicago.html
Conference date: 4 February 2026
ISBN: 978-1-80590-635-3(Print)/978-1-80590-636-0(Online)
Editor: Marwan Omar
Volume 224February 2026
Find articlesProceedings of CONF-SEML 2026 Symposium: Learning and Decision Making in Multi Agent Software Systems
Conference website: https://www.confseml.org/bath.html
Conference date: 14 April 2026
ISBN: 978-1-80590-597-4(Print)/978-1-80590-598-1(Online)
Editor: Mustafa İSTANBULLU , Jie Zhang
Volume 223February 2026
Find articlesProceedings of CONF-SEML 2026 Symposium: Importance of Machine Learning Methods and Analysis in Engineering
Conference website: https://www.confseml.org/astana.html
Conference date: 20 March 2026
ISBN: 978-1-80590-591-2(Print)/978-1-80590-592-9(Online)
Editor: Mian Umer Shafiq , Mustafa İSTANBULLU
Announcements View all announcements
Applied and Computational Engineering
We pledge to our journal community:
We're committed: we put diversity and inclusion at the heart of our activities...
Applied and Computational Engineering
The statements, opinions and data contained in the journal Applied and Computational Engineering (ACE) are solely those of the individual authors and contributors...
Indexing
The published articles will be submitted to following databases below:






