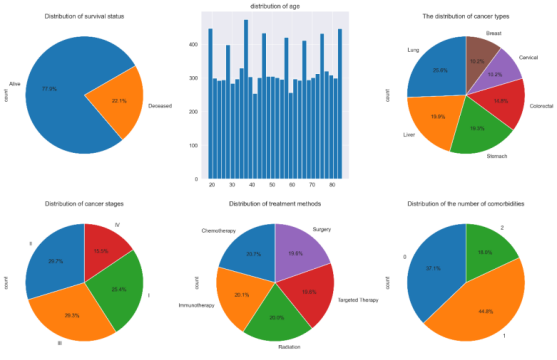
Cancer remains a major public health challenge in China. This study analyzed a multi-center cohort of 10,000 Chinese cancer patients to evaluate real-world survival outcomes and treatment effectiveness. Kaplan–Meier estimation and Cox proportional hazards regression were employed to assess associations between patient characteristics, treatment types, and overall survival. Survival analysis showed no significant difference in overall survival among six major cancer types (lung, liver, stomach, colorectal, cervical, breast) or among five treatment modalities (chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, surgery). Cancer stage was the strongest prognostic factor: patients with Stage I–II disease had 100% five-year survival, while Stage III–IV survival fell to about 6%. Metastasis, larger tumor size, and geographic region were independent risk factors for death after adjusting by other covariates, but not modality of treatment. The results highlight the importance of timely diagnosis and availability of healthcare services in different areas are important targets of China's cancer prevention programs.