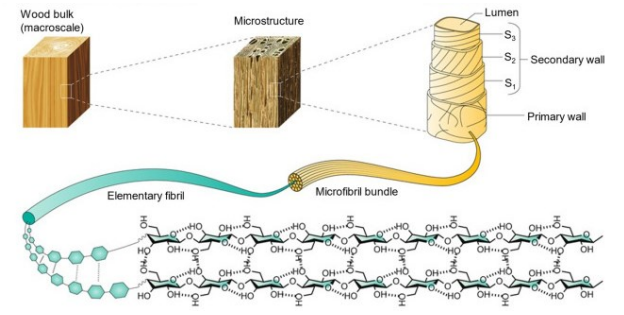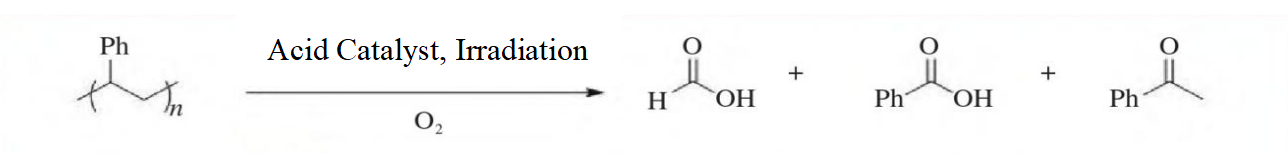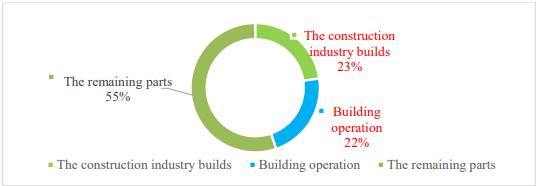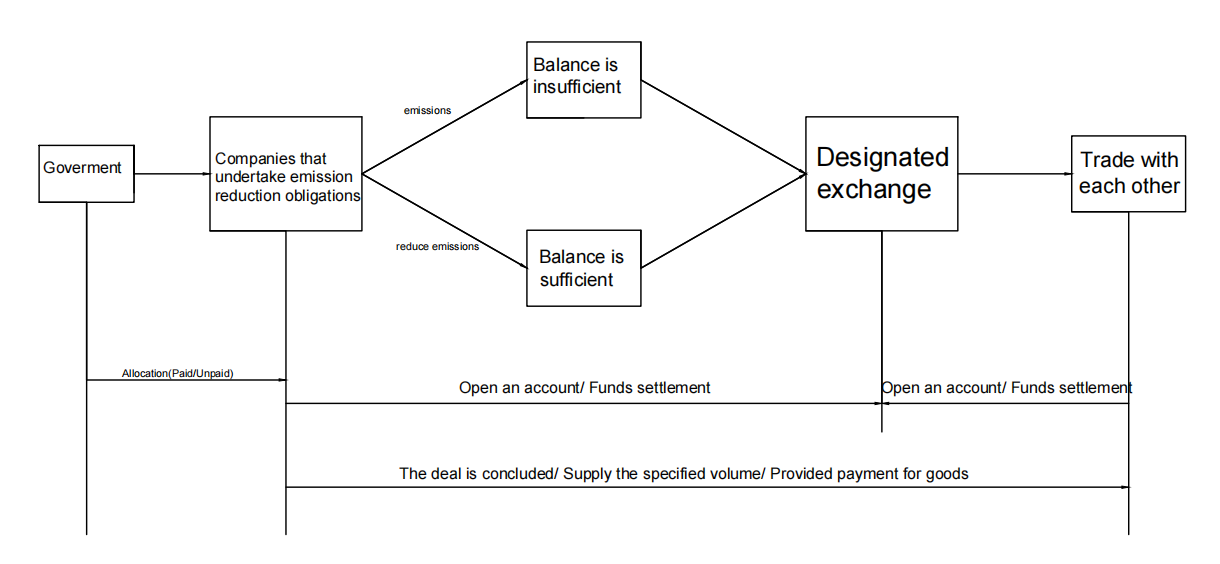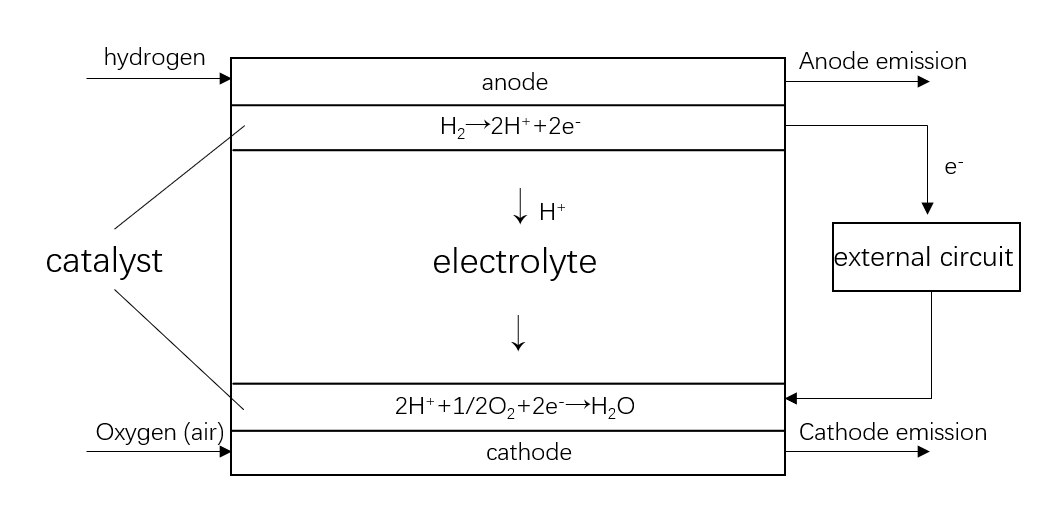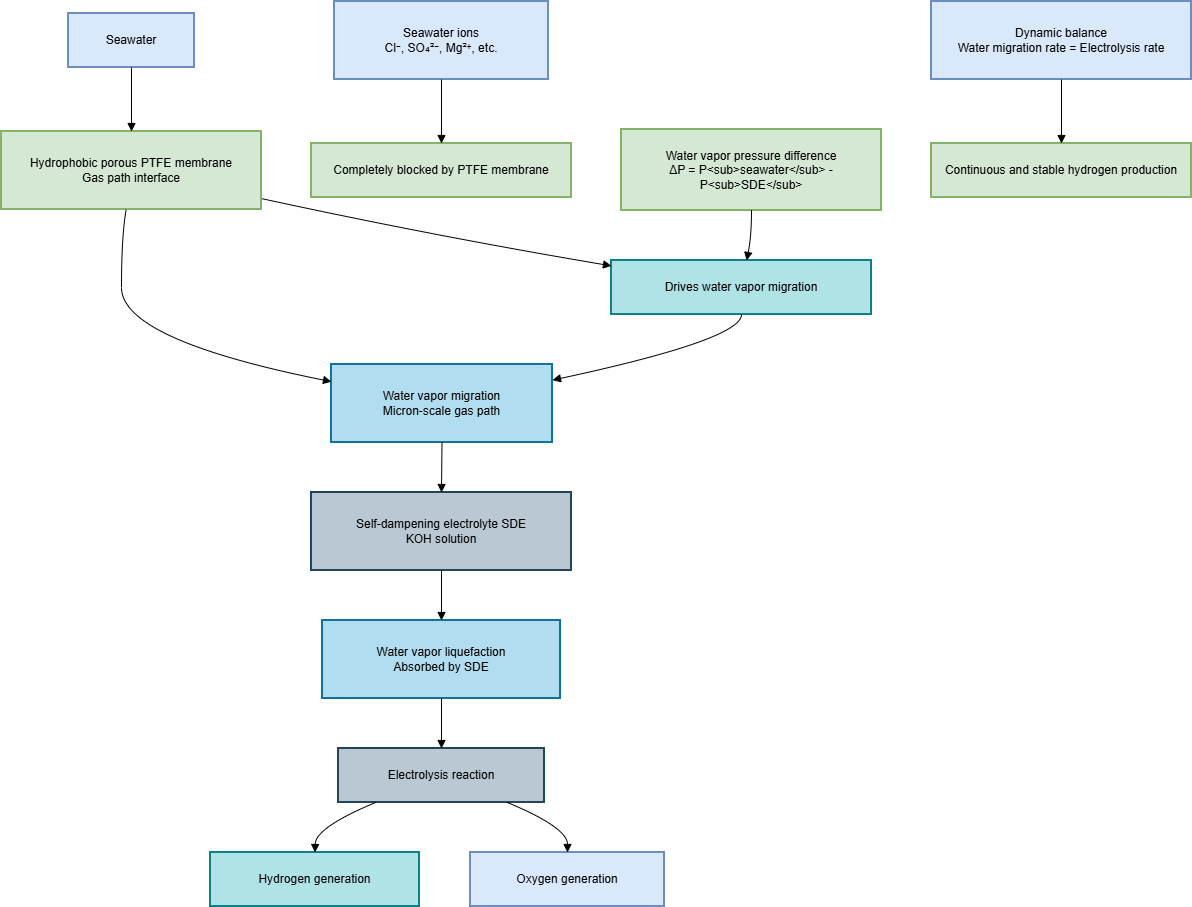
The in-situ direct electrolysis of seawater for hydrogen production without desalination is a promising green hydrogen production method. Its core lies in achieving efficient blocking of seawater ions and efficient supply of pure water through the phase transition migration mechanism. This paper systematically reviews the principal evolution, key material optimization, and system integration progress of this technology, and focuses on analyzing the impact of waterproof breathable membranes, self-hydrating electrolytes, and efficient catalysts on the system performance. The research shows that this technology has achieved coupling operation with offshore wind power and has demonstrated good stability and adaptability in real marine environments. Although there are still challenges in catalyst cost and system scale-up, through the improvement of standard systems, the establishment of industrial chains, and the innovation of application models, this technology is expected to achieve commercial application within the next decade. In addition, continued cross-disciplinary collaboration is expected to further accelerate the technological refinement and practical deployment of seawater electrolysis systems.