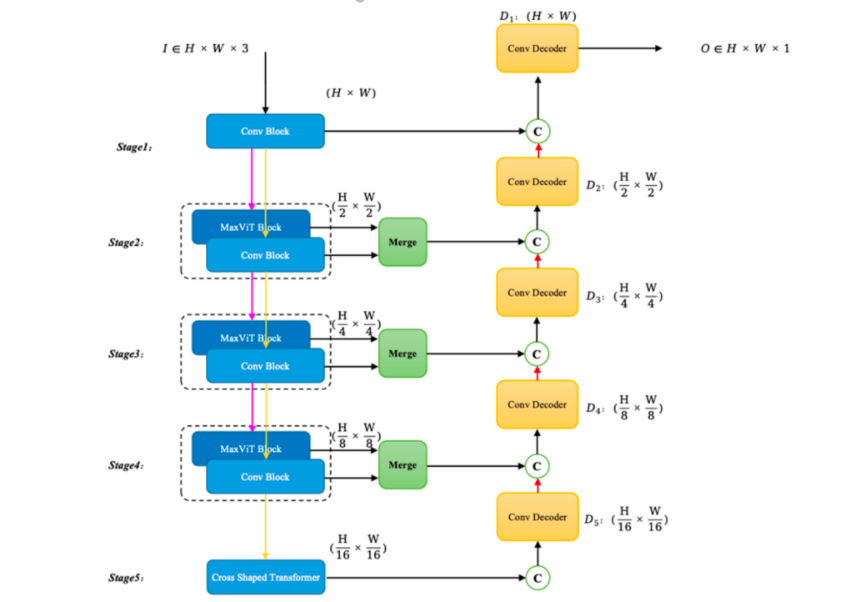
The advancement of colorectal cancer emphasizes how important it is for colonoscopic imaging to accurately segment polyps. Learning-based techniques have made significant progress in the field of polyp medical image segmentation; however, recurring issues such as the identification of small object segments, poorly defined lesion boundaries, and complex backgrounds still exist. In order to overcome these constraints, we introduce CDBT-Unet, a brand-new framework that enhances segmentation performance by integrating two significant innovations. Initially, the transformer layer's convolutional prior speeds up convergence and extracts the fine-grained local texture that is essential for tiny flat polyps. By prioritizing horizontal-vertical background relationships through cross-shaped attention, it improves boundary delineation in complex backgrounds by reducing computation and accelerating convergence. The intricate background and edge blurring issue of polyp segmentation is well-considered in this point. Second, in order to improve accuracy, our dual-path encoder uses the MaxViT block to strategically balance global dependency modeling and local feature preservation. Combining multilevel feature fusion with coordinate space focus mechanisms and channel refinement improves edge response in multiscale fusion. The issue of boundary blurring is the main focus. Under the same experimental setup, our model outperforms the state-of-the-art ConDseg model by 3.72% and the baseline (TransUnet) by 7.32% in terms of Dice scores when tested on the Kvasir-SEG and CVC-ClinicDB datasets. Even in the presence of motion artifacts or low contrast, the framework demonstrates exceptional robustness in segmenting polyps of various sizes. Furthermore, the attention maps that were produced enhanced interpretability and gave physicians practical knowledge about how to make decisions when modeling.