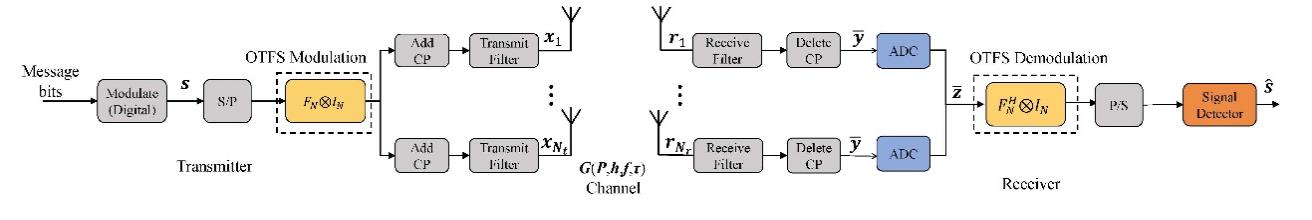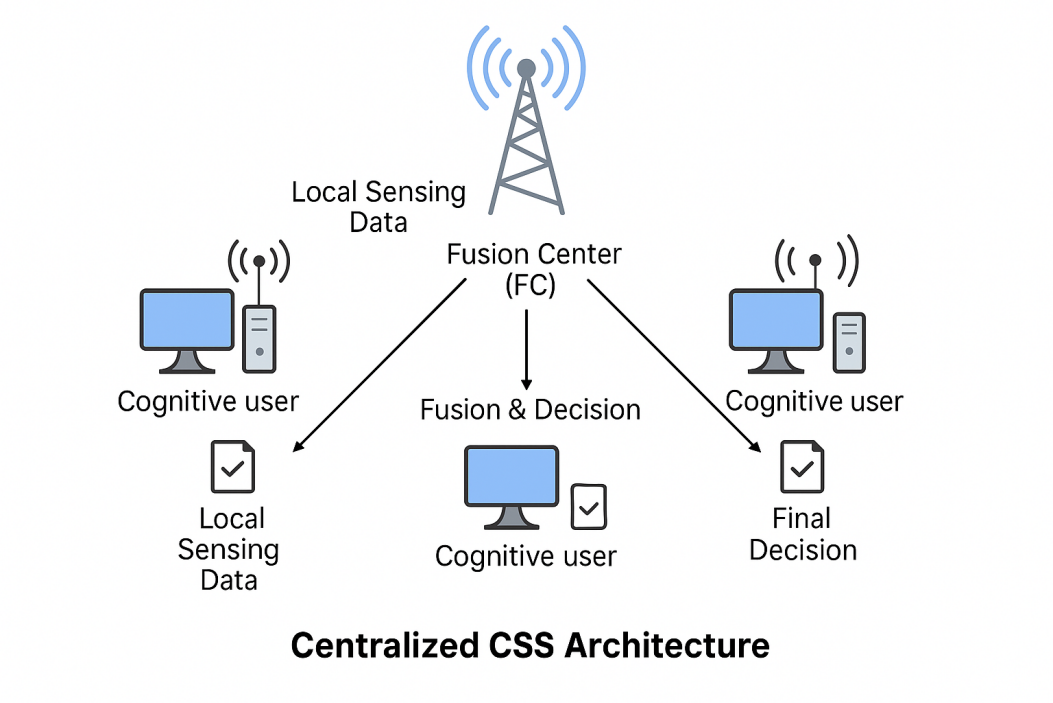
Cooperating Spectrum Sensing(CSS) is the cornerstone of dynamically shared spectrum access in CRN. But it’s hampered by subpar conditions like noise that’s not right, a lack of data, and hardware issues too. These defects distort sensing data and cause the “SNR wall” effect, seriously degrade the performance of traditional sensing algorithms. To solve those issues this article gives a comprehensive review on CSS, the survey is started with creating a common analysis platform which will isolate the key problems then we will be taking a look at them from 3 points of view: noisiness, Data Integrity, Hardware Impairment Based on the aforementioned framework, we do a comprehensive overview and comparison of 3 major categories of mainstream solutions - statistical learning method based on the generalized Gaussian mixture model and meta-heuristic optimization; deep learning approach integrated with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Transformer architecture; and Deep Reinforcement Learning-based communication-sensing co-design strategy. The evaluations cover several areas like the kind of deformities it addresses, use of prior knowledge, complexity in processing, and whether it can work in actual situations. This complete examination leads to a good plan that covers finding things, missing them accidentally, and doing well even if there’s some trouble. our analysis tells us how good each method is, what trade-offs they have, and when they work best. This gives us simple rules about which methods to use and how to make them. In the end, we give potential directions for future research, which are new paradigms for adaptive and privacy-preserving CSS in the dynamic spectrum-sharing, heterogeneous network integration, and increasing privacy-security environment.