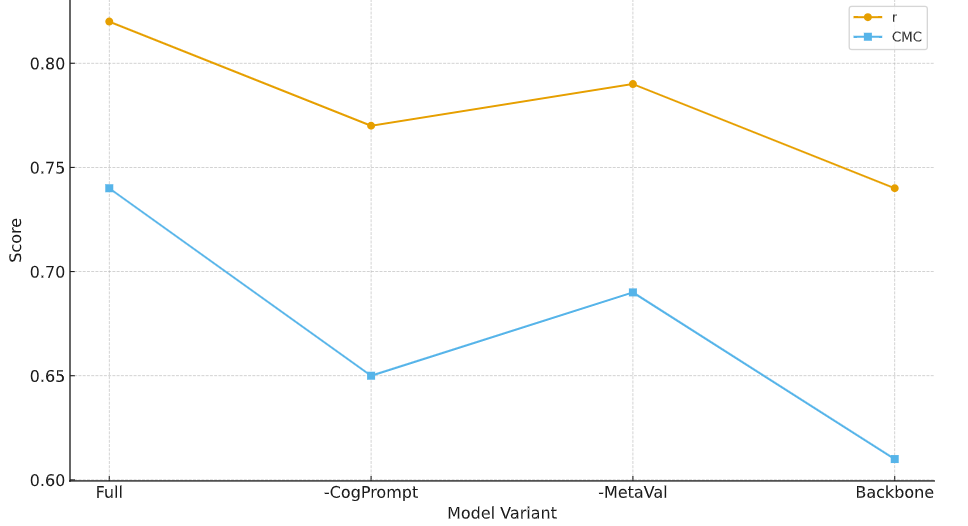
Metaphor translation quality estimation requires models to track shifts in conceptual structure across languages, rather than simply comparing surface similarity. This study proposes a cognitive-linguistics-driven prompting framework that injects conceptual metaphor information into a dual-encoder architecture and calibrates its decisions through a meta-learned transferable validator. Cognitive prompt templates encode source–target domain mappings, imageability, and contextual constraints, while a contrastive objective encourages consistent alignment between metaphorical inputs and their translations. A meta-learning layer further adapts validation weights to new metaphor families and language pairs with limited supervision. Experiments on two bilingual datasets (English–Chinese and English–Spanish, 7,420 and 6,985 annotated sentence pairs respectively) show that the framework improves correlation with human ratings, conceptual mapping consistency, and metaphor retention in both in-domain and zero-shot transfer settings. Quantitative analyses and ablation studies indicate that cognitive prompting contributes most of the gains in conceptual alignment, whereas transferable validation stabilizes performance under domain and language shifts. The findings suggest that cognitively grounded prompting can bridge linguistic theory and neural evaluation, providing interpretable and robust decisions for metaphor translation quality estimation across languages.