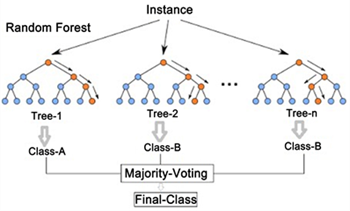
This study presents a machine learning method for regression prediction of used sailboat prices. The dataset contains attributes such as brand, length, year, and listing price of the sailboat, and the dataset is preprocessed by removing irrelevant fields and normalizing the data. A random forest model is constructed and evaluated against several models such as gradient boosting and neural networks through k-fold cross-validation. Random Forest performs well compared to other models. The ensemble approach of the algorithm effectively modeled the complex nonlinear relationships in the data. Rigorous validation ensures the generalizability of the model. The Random Forest model outperforms traditional manual assessments in terms of the accuracy of price assessments. This data-driven solution allows customers to value sailboats on their own and avoid paying excessive fees. It also allows sailboat companies to develop automated pricing systems to speed up operations. This research provides a powerful machine-learning approach for accurately predicting used sailboat prices. These techniques can be extended to other regression tasks. Further work includes refining the model and deploying real-world applications.