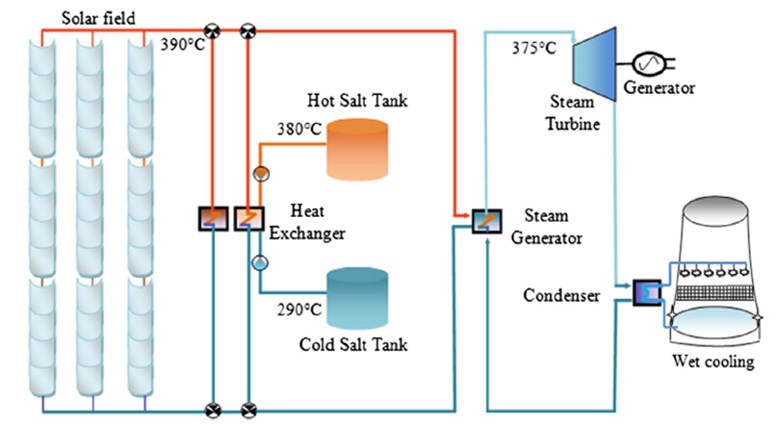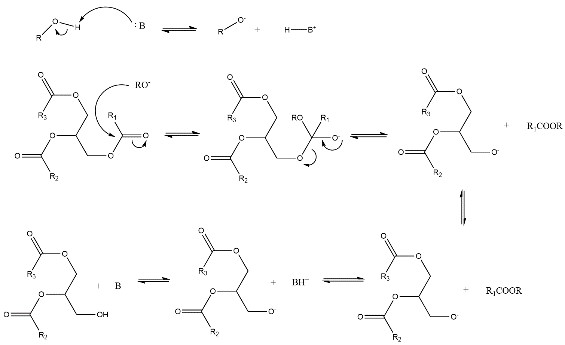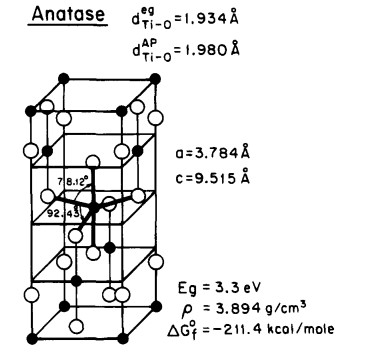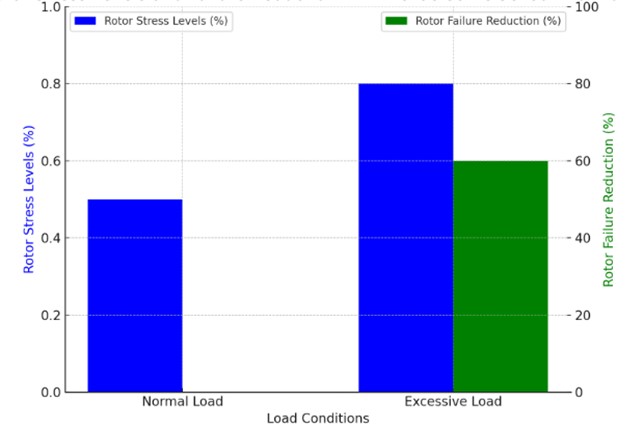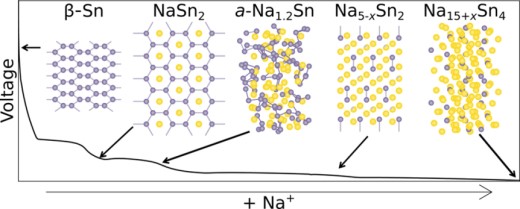
Sodium ion batteries (SIBs) is considered as a promising battery to replace lithium ion battery (LIBs). Sn-based electrode materials have been widely studied because of their high theoretical capacity, good safety performance and good environmental compatibility. However, due to the serious volume change, slow dynamic response and low coulombic efficiency, the battery capacity decreases rapidly, which still needs great improvement. In this paper, the types of Sn-based electrodes up to now are reviewed, and their electrode reaction principles are briefly described, and the advantages of various electrodes are summarized. At the same time, the improvement methods of Sn-based electrodes are further summarized. Finally, the Sn-based materials are summarized and the research direction of Sn-based electrodes in the future is prospected.