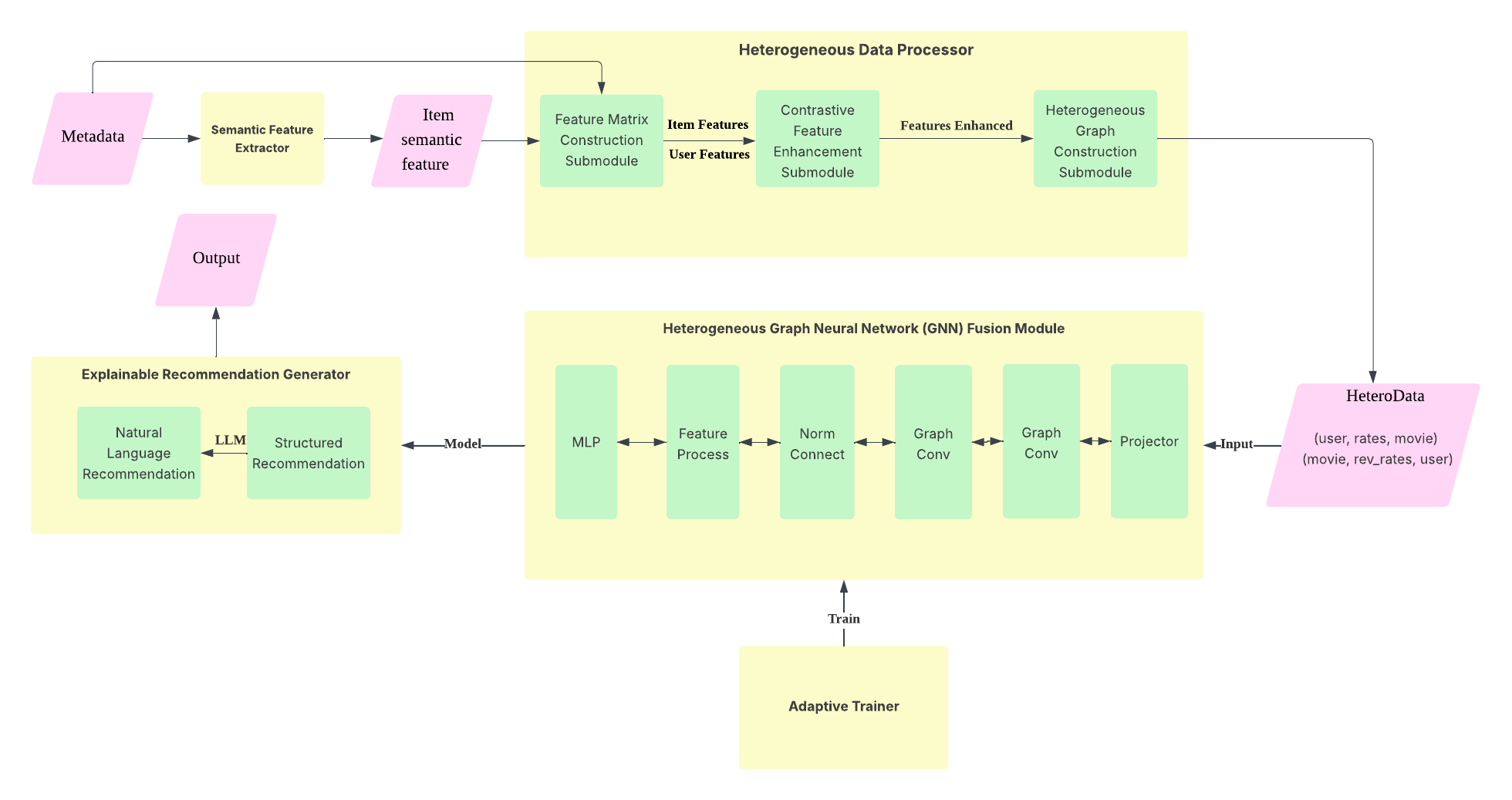
This paper proposes GLEM-Rec, a cross-modal recommendation framework integrating large language models with graph neural networks, effectively addressing three major challenges in traditional recommendation systems: semantic-graph structure feature alignment, long-tail item recommendation, and explainability. The framework consists of five core modules: semantic feature extractor, heterogeneous data processor, heterogeneous GNN integrator, adaptive trainer, and explainable recommendation generator, achieving complementary advantages between LLM's deep semantic understanding and GNN's high-order relationship modeling. Through multi-objective optimization strategies, GLEM-Rec achieves a balance between prediction accuracy, recommendation diversity, personalization, and long-tail coverage. Experiments based on the Movies Dataset demonstrate that this framework significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving an RMSE of 0.9122, coverage rate of 0.7723, and long-tail item recommendation performance of 0.9851, comprehensively surpassing traditional baseline models. System ablation experiments confirm the necessity and effectiveness of each functional module, validating the critical contribution of semantic and graph structure feature collaboration to recommendation system performance. This research not only provides new theoretical support for cross-modal recommendation systems but also offers effective technical solutions for key challenges in recommendation system practice.