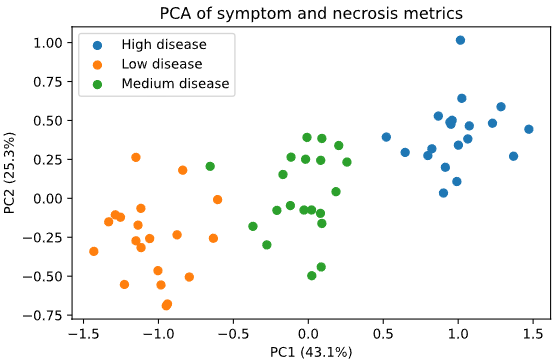
With the progress in chemo-biological imaging technology, accurate molecular site segmentation and ligand detection with rare data has become an essential mission in drug screening, protein engineering, and early-stage disease detection. Traditional deep networks require extensive annotated data and fail to generalize well with multiple modalities jointly. In this work, we present the Few-shot Multimodal Chemo-Biological Imaging Framework (CMA-FSL), which combines chemical mass spectrometry and biological microscopy by cross-modal attention and adopts metric-based prototypical learning to rapidly learn with only a few data points. Experiment results on the ChemoBio-FS dataset show that our model outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of Dice score, IoU score, and Top-1 accuracy with more than 6% improvement in 5-way 5-shot evaluation settings, with results of 82.4%, 76.8%, and 86.9% respectively, validating the practicability and efficacy of multimodal learning in chemo-biological imaging with only a few data points, and opening an new thought and paradigm on small sample molecular diagnostic and intelligence drug discoveries.
Research Article
Open Access