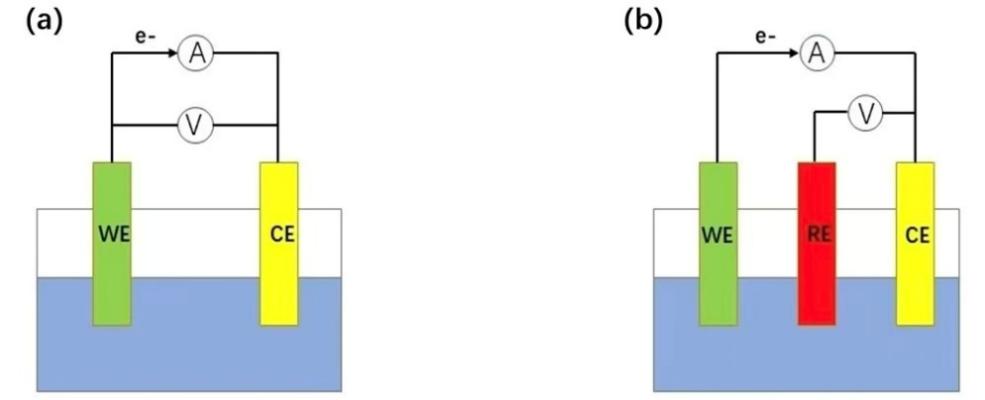
In clinical practice, monitoring physiological indicators is essential for evaluating human health. Conventional medical devices can detect many of these signals, but their responses are often limited by insufficient selectivity and unstable output, which restricts their reliability. Electrochemical sensors have therefore attracted extensive interest in biomedical analysis as tools for assessing health status. By combining simple operation with high stability, sensitivity, and quantitative capability, electrochemical biosensors offer a promising platform for medical testing. This review provides an overview of recent developments in electrochemical biosensors for the detection of key biological targets, with a particular focus on viruses, glucose, and cancer cells. We summarize representative detection strategies and sensing materials, and highlight the main technical challenges encountered in practical applications. Finally, we discuss potential directions for the future development of electrochemical sensors in biomedical diagnostics.