About ACEThe proceedings series Applied and Computational Engineering (ACE) is an international peer-reviewed open access series that publishes conference proceedings from various methodological and disciplinary perspectives concerning engineering and technology. ACE is published irregularly. The series contributes to the development of computing sectors by providing an open platform for sharing and discussion. The series publishes articles that are research-oriented and welcomes theoretical and applicational studies. Proceedings that are suitable for publication in the ACE cover domains on various perspectives of computing and engineering. |
| Aims & scope of ACE are: ·Computing ·Machine Learning ·Electrical Engineering & Signal Processing ·Applied Physics & Mechanical Engineering ·Chemical & Environmental Engineering ·Materials Science and Engineering |
Article processing charge
A one-time Article Processing Charge (APC) of 450 USD (US Dollars) applies to papers accepted after peer review. excluding taxes.
Open access policy
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. (CC BY 4.0 license).
Your rights
These licenses afford authors copyright while enabling the public to reuse and adapt the content.
Peer-review process
Our blind and multi-reviewer process ensures that all articles are rigorously evaluated based on their intellectual merit and contribution to the field.
Editors View full editorial board

United Kingdom
anil.fernando@strath.ac.uk

United Kingdom
yilun.shang@northumbria.ac.uk

Portsmouth, UK
ella.haig@port.ac.uk

The United Arab Emirates
moayad.aloqaily@mbzuai.ac.ae
Latest articles View all articles
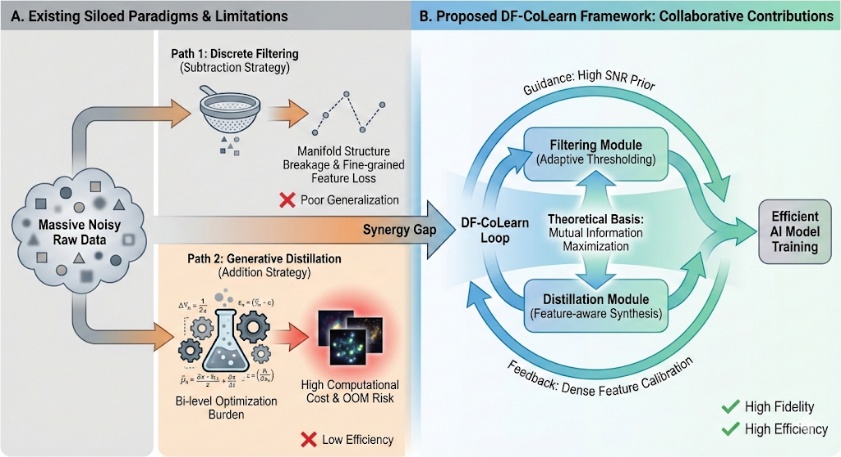
In order to solve the endogenous contradiction between the data scale dividend and the diminishing marginal effect of computing power in large-scale deep learning, this paper proposes a collaborative learning framework for large-scale Dataset distillation and Filtering (DF-CoLearn). By constructing a dynamic feedback closed loop based on bi-level optimization and mutual information maximization, the Pareto optimality between training efficiency and model generalization ability is realized, which provides a new theoretical perspective and technical path for green and efficient AI model training.

 View pdf
View pdf


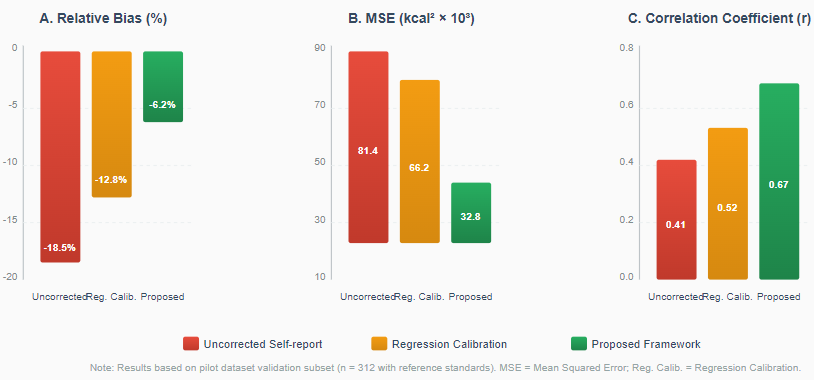
Measuring dietary exposure is the key aspect of nutritional epidemiology in order to find cause and effect relationships between nutrition and long-term illnesses. Nevertheless, self-reported nutrition assessment tools e.g. food frequency questionnaires and dietary recalls provide systematic underreporting as well as random error in nutrition assessment that considerably reduce the regression coefficients of exposure-outcome relationships and even obscure true diet-health effects under measurement errors. The current corrections methods conducted on small reference samples and depending on the assumptions of linearity are capable of treating variations of errors in multimodal data of great dimensions. We are going to present an idea of self-supervised multimodal representation learning, that is, an error-reducting dietary exposure measure, where dietary text logs and wearable sensor data are modeled jointly and learns discriminative features highly correlated with true intake through cross-modal contrastive learning and masked reconstruction, trained over multi-view representations to produce an exposure-corrected dietary energy and nutrient consumption estimate using a unified latent space, and produce an exposure-corrected dietary text log estimate using a unified latent space.

 View pdf
View pdf


Image-based artificial intelligence models are widely applied in data science tasks such as image classification, object recognition, and visual content generation. In practice, model outputs are often regarded as reliable once acceptable accuracy levels are achieved on benchmark datasets. However, empirical evidence shows that image-based AI systems frequently exhibit structured and non-random error patterns. In image generation tasks, errors commonly arise from an overreliance on statistical correlations learned from training data, limited semantic grounding, and weak constraints on physical and contextual consistency. These limitations can lead to outputs that appear visually coherent while containing incorrect or non-existent objects, implausible spatial relationships, or violations of basic visual logic. From a data science perspective, such errors are often underexamined because evaluation practices rely heavily on aggregate accuracy metrics and benchmark performance, which tend to obscure localized error concentration and output variability. This study conducts a structured analysis of error patterns and output limitations in image-based AI systems by examining misclassification behavior, generation inconsistencies, and evaluation blind spots observed under realistic data conditions. The findings indicate that understanding AI image generation errors requires focusing on error structure and underlying generation mechanisms rather than relying solely on summary performance measures.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the widespread deployment of machine learning models in high-stakes decision-making contexts, their inherent opacity—often termed the "black-box" problem—has raised significant concerns regarding interpretability and reliability. This paper presents a systematic and comprehensive literature review examining the convergence of interpretable machine learning and statistical inference. This paper synthesizes foundational concepts, methodological frameworks, theoretical advancements, and practical applications to elucidate how statistical tools can validate, enhance, and formalize machine learning explanations. This review critically analyzes widely adopted techniques such as SHAP and LIME, and explores their integration with statistical inference tools, including hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, Bayesian methods, and causal inference frameworks. The analysis reveals that integrated approaches significantly improve explanation credibility, regulatory compliance, and decision transparency in critical domains, including healthcare diagnostics, financial risk management, and algorithmic governance. However, persistent challenges remain in theoretical consistency, computational efficiency, evaluation standardization, and human-centered design. This paper concludes by proposing a structured research agenda focusing on unified theoretical frameworks, efficient algorithmic implementations, domain-specific evaluation standards, and interdisciplinary collaboration strategies to advance the responsible development and deployment of explainable AI systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


Volumes View all volumes
Volume 228February 2026
Find articlesProceedings of the 4th International Conference on Software Engineering and Machine Learning
Conference website: https://www.confseml.org/index.html
Conference date: 26 June 2026
ISBN: 978-1-80590-533-2(Print)/978-1-80590-534-9(Online)
Editor: Mustafa İSTANBULLU
Volume 227February 2026
Find articlesProceedings of CONF-SEML 2026 Symposium: Computational Analysis and Modeling in Complex Intelligent Systems
Conference website: https://www.confseml.org/guildford.html
Conference date: 26 June 2026
ISBN: 978-1-80590-469-4(Print)/978-1-80590-470-0(Online)
Editor: Mustafa İSTANBULLU , Roman Bauer
Volume 226February 2026
Find articlesProceedings of CONF-SEML 2026 Symposium: Multimodal Data Acquisition: Applications in Physiological and Behavioral Research
Conference website: https://www.confseml.org/adana.html
Conference date: 20 May 2026
ISBN: 978-1-80590-637-7(Print)/978-1-80590-638-4(Online)
Editor: Mustafa İSTANBULLU
Volume 225February 2026
Find articlesProceedings of CONF-SPML 2026 Symposium: The Artificial Intelligence Tools & Applications
Conference website: https://www.confspml.org/chicago.html
Conference date: 4 February 2026
ISBN: 978-1-80590-635-3(Print)/978-1-80590-636-0(Online)
Editor: Marwan Omar
Announcements View all announcements
Applied and Computational Engineering
We pledge to our journal community:
We're committed: we put diversity and inclusion at the heart of our activities...
Applied and Computational Engineering
The statements, opinions and data contained in the journal Applied and Computational Engineering (ACE) are solely those of the individual authors and contributors...
Indexing
The published articles will be submitted to following databases below:





