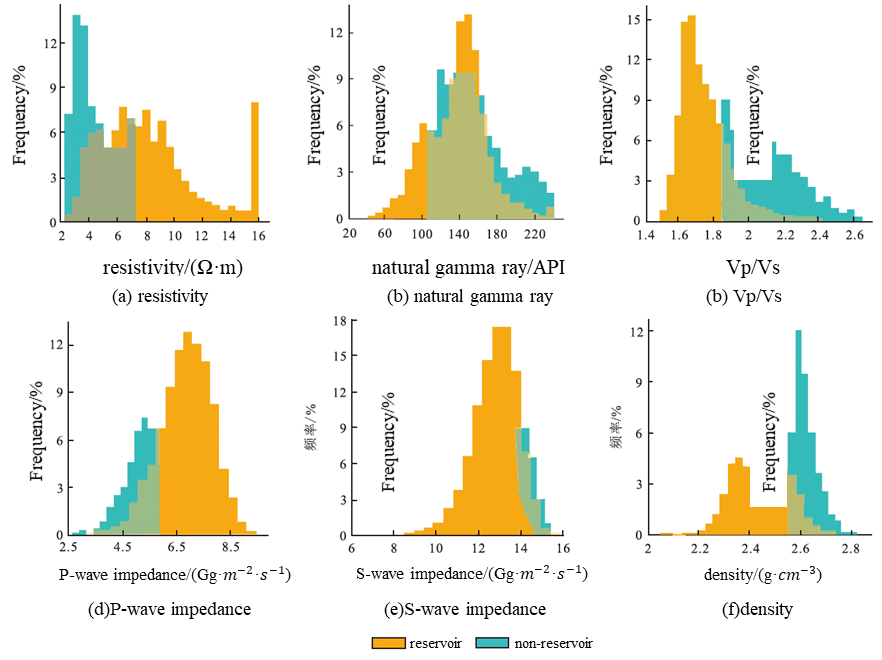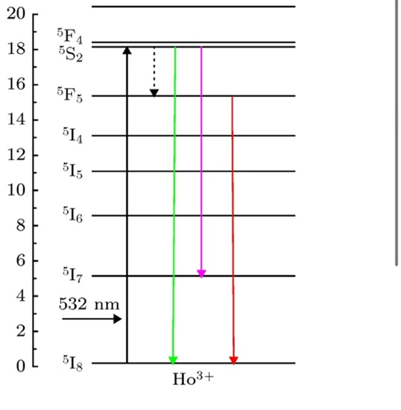
This study aims to explore the application of Ho³⁺-doped ZBLAN glass in U⁺-band (1700–1800 nm) fiber lasers. This spectral region possesses low water absorption and minimal biological tissue scattering, making it broadly applicable for deep biological tissue imaging, molecular spectroscopy identification, gas sensing, and military optoelectronic systems, thus significantly advancing optical communication, industrial processing, and biomedical fields. Using MATLAB simulation software, we constructed a theoretical model for a Ho³⁺-doped ZBLAN fiber laser based on rate equations and power propagation equations. Simulation results demonstrated a linear increase in output power with increasing pump power under conditions of fiber length 1.2 m, doping concentration 6.0×10²⁵ m⁻³, and pump wavelength of 1150 nm. Specifically, a maximum laser output power of approximately 1.28 W was achieved at a pump power of 20 W. Furthermore, the simulation results verified the consistency of the physical mechanisms of the model and the laser establishment process, with a threshold pump power of approximately 1.7 W and a slope efficiency of 6.7%. This research provides theoretical support and practical reference for the design and performance optimization of efficient U⁺-band fiber lasers. Future work could further optimize doping concentration, pumping structure, and fiber core design to enhance optical-optical conversion efficiency and output power, meeting higher power application demands and promoting technological advancements in related fields.