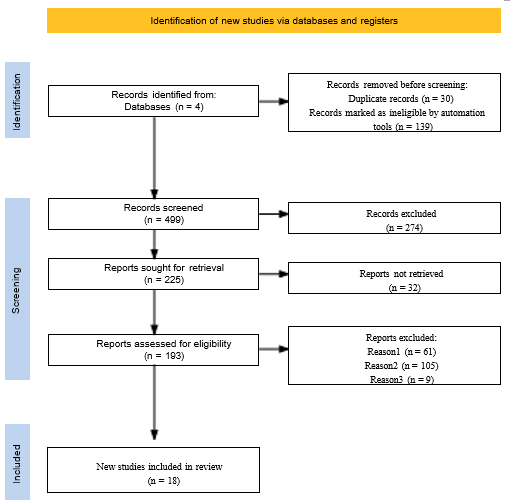
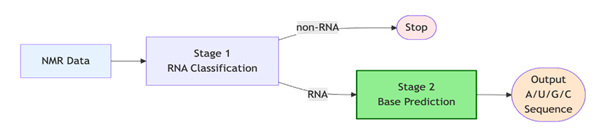
Medical image processing is a very important role in modern healthcare diagnosis and treatment. However, traditional manual analysis faces challenges like high variances, low efficiencies and low accuracies. Recently, deep learning techniques like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have rapidly improved and achieved remarkable success and improvements in areas like medical image classification, segmentation, and detection tasks due to their powerful feature extraction capabilities. Nevertheless, CNNs exhibit limitations in modeling global contextual information and rely heavily on large-scale annotated datasets. The emergence of Vision Transformers (ViTs) offers a new perspective by effectively modeling global image features through self-attention mechanisms. Hybrid models that combine the strengths of CNNs and Transformers have thus become a research hotspot. This paper aims to make reviews for fusion methods between CNN and Transformers in medical image processing, including typical strategies such as early fusion, intermediate fusion, and late fusion, and summarizes their application performance and advantages in various tasks. Experimental results show that hybrid models are able to show better performance than areas like single-architecture models in terms of accuracy, generalization ability, and adaptability to complex tasks. Finally, this paper discusses the future challenges faced by hybrid models in terms of data scarcity, computational efficiency, and interpretability, and outlines future research directions.
Research Article
Open Access