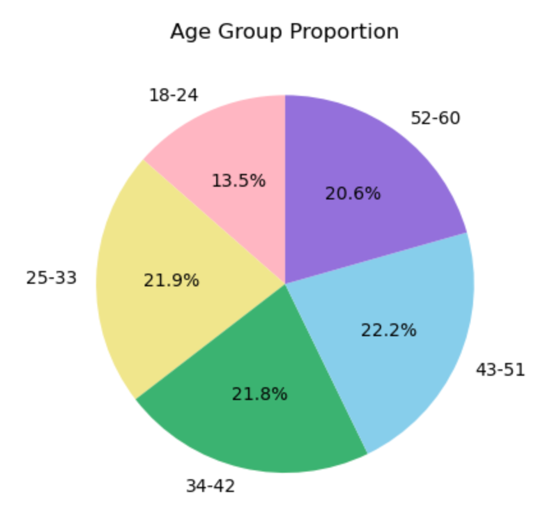
Understanding the correlation between various risk factors and depression is important for developing personalized and effective treatment plans, especially for those at risk of recurrent or chronic depression. Current literature and predictive models identify pressure and age as primary risk factors, in addition to other factors such as financial stress, employment or student status, and suicidal thoughts. This approach emphasizes the importance of considering a range of interrelated factors that may influence each other and compound over time. Particular attention should be paid to vulnerable and marginalized populations, who are disproportionately affected and have higher prevalence of depression, emphasizing the need for individualized treatment and targeted interventions. High accuracy predictive models are used to assess the impact of individual and combined risk factors, providing a tool for identifying people at risk of depression before symptoms such as somatization become fully manifest. Early identification can lead to more proactive interventions, improved clinical outcomes, and a reduction in the overall impact of depression on society.